In a previous post I made I showed you how to upload a file from a URL using a PHP script. You can view this post here.
Now I will show you how to take this a step further and upload multiple files from multiple URLs or uploaded from the user’s computer.
Because we will have multiple files to upload we are going to want to make an array of these files that include all their attributes. Then we’ll process each file at a time and based on whether it is coming from a URL or the user’s hard drive, we will upload it accordingly.
Here is a preview of what our form will look like:
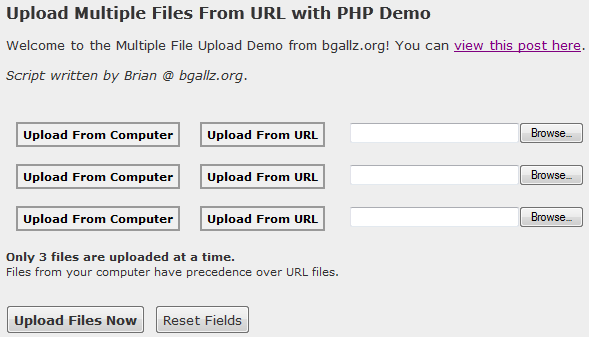
Here is our HTML for this form on index.php:
<form action="./index.php?do=upload" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data" name="upload_files_form">
<div id="upload_files">
<div id="upload_file_1">
<div>
<button id="1_computer_button" name="upload_type_computer" type="button" onclick="hideElement('1_upload_url'); showElement('1_upload_computer')">Upload From Computer</button>
<button id="1_url_button" name="upload_type_url" type="button" onclick="hideElement('1_upload_computer'); showElement('1_upload_url')">Upload From URL</button>
</div>
<div>
<div id="1_upload_computer">
<input type="file" name="files_hdd[]" size="30" />
</div>
<div id="1_upload_url" style="display:none">
<input type="text" name="files_url[]" size="30" maxlength="100" value="http://" onfocus="if(this.value == 'http://') this.value = '';" id="1_input_url" />
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div id="upload_file_2">
<div>
<button id="2_computer_button" name="upload_type_computer" type="button" onclick="hideElement('2_upload_url'); showElement('2_upload_computer')">Upload From Computer</button>
<button id="2_url_button" name="upload_type_url" type="button" onclick="hideElement('2_upload_computer'); showElement('2_upload_url')">Upload From URL</button>
</div>
<div>
<div id="2_upload_computer">
<input type="file" name="files_hdd[]" size="30" />
</div>
<div id="2_upload_url" style="display:none">
<input type="text" name="files_url[]" size="30" maxlength="100" value="http://" onfocus="if(this.value == 'http://') this.value = '';" id="2_input_url" />
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div id="upload_file_3">
<div>
<button id="3_computer_button" name="upload_type_computer" type="button" onclick="hideElement('3_upload_url'); showElement('3_upload_computer')">Upload From Computer</button>
<button id="3_url_button" name="upload_type_url" type="button" onclick="hideElement('3_upload_computer'); showElement('3_upload_url')">Upload From URL</button>
</div>
<div>
<div id="3_upload_computer">
<input type="file" name="files_hdd[]" size="30" />
</div>
<div id="3_upload_url" style="display:none">
<input type="text" name="files_url[]" size="30" maxlength="100" value="http://" onfocus="if(this.value == 'http://') this.value = '';" id="3_input_url" />
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<input type="submit" name="submit" value="Upload Files Now" onclick="showUploadDiv()" /> <input type="reset" name="reset" value="Reset Fields" />
<p> </p>
<div id="uploading" style="display:none">
</div>
</form>This form contains three file inputs, either uploaded from the user’s computer, or given by a URL to a file. There are two buttons for each input which enable and disable the HDD or URL upload options. Now, I haven’t made the script to completely disable the URL input once a file has been selected from the user’s computer, so when the form is submitted it will check for uploaded files first over files being gathered from a URL. So you will want to include that on your main page so users know you can only upload three files at a time here, not six.
The form includes the animated loading gif feature which I posted here:
https://bgallz.dev/1140/how-to-make-animated-loading-gif/
You’ll notice on the submit button it activates the Javascript function “showUploadDiv().” This function changes the display style setting on the uploading div and then fills it with some text and the animated loading image.
I also have used some jQuery for the buttons to be used effectively:
<script src="jquery-1.7.2.min.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
$(document).ready(function(){
var clickedClass = "selected";
var buttons = "#upload_files button";
$(buttons).click(function() {
$(this).addClass(clickedClass).siblings().removeClass(clickedClass);
});
});
</script>What this jQuery says is to add the class “selected” – from clickedClass – to the current button that is being clicked, and remove that class name from all other buttons within the current parent’s sibilings. Sounds a little complicated, but it’s very simple. The buttons are loaded from “#upload_files button” – so thats all the button elements within the div ID “upload_files.”
Now finally for the PHP of the script. On index.php we include the following in the header:
$valid_exts = array(
"gif","png","jpeg","jpg",
"image/gif","image/jpeg","image/png","image/jpg"
); // array of valid file extensions
$max_file_size = 32; // file size in kb
$upload_dir = "files/"; // directory to upload to with trailing slash
$upload_result = "";
if(isset($_GET['do']) && $_GET['do'] == "upload"){
$upload_result = run_upload_form();
}So when the form is submitted – which is sent to “index.php?do=upload” – we run the function run_upload_form() and set the $upload_result to its returned value.
The key variables defined at the beginning of the script are there for you to modify as you need them. Of course you can modify the function itself to output different values as you need them to be. Currently the script checks against the following before uploading:
- Valid extension type (image files by default)
- File size limit (32KB by default)
- Upload directory exists and is writable
- URL validation for remote file size and type
To view the rest of the PHP as well as the Javascript and CSS styles you must download the script.
Download the script free here.
Multiple File Upload with HTML5
A new feature of HTML 5 is the ability to use a multiple file upload field. This is extremely simple with HTML 5. You basically create an input tag with type = file and the multiple attribute applied.
Here is an example:
<form action="upload.php" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
Upload Files: <input type="file" name="upload_files[]" multiple="multiple" />
<input type="submit" value="Submit" name="submit" />
</form>This will create the following:
This may look like a regular file upload input from standard HTML however when you click the “Browse…” button to look for files on your computer, you can select multiple files by Shift+Clicking on the desired files grouped together, or alternatively Ctrl+Clicking to select individual scattered files. This only works for files coming from your computer of course, so to upload multiple files from URL, you will need a script like the one above.
Here is a screenshot of the browse window. You can select multiple files as you can see they are highlighted, and listed in order in the “File name:” input.
For this multiple file upload, the PHP is much simpler. We simply run the upload like we would for the first example, only we don’t have to worry about URL files or checking an array of files. The HTML already loads the files into an array for us when PHP checks the $_FILES[‘upload_files’].
Here is how it looks…
<?php
// upload multiple files from HTML5 multiple files input
if(isset($_POST['submit']))
{
$valid_exts = array("image/gif","image/jpeg","image/png","image/jpg"); // image files
$max_size = 20480; // max size in kb (2kb default)
$directory = "./files/"; // upload directory
$upload_files = $_FILES['upload_files'];
$files_uploaded = array(); // successful uploads
if(is_array($upload_files))
{
foreach($upload_files as $file)
{
if(in_array($file["type"],$valid_exts))
{
if($file["size"] <= $max_size)
{
// file is valid type and size, let's upload
if(move_uploaded_file($file["tmp_name"],$directory . $file["name"]))
{
$files_uploaded[] = '<a href="'.$directory.$file["name"].'" target="_blank">'.$file["name"].'</a>';
}
} else { return "File size too large. Max file size is: ". ($max_size / 1024) . " KB."; }
} else { return "Only image file types may be uploaded."; }
}
return "". count($files_uploaded) ." files out of ". count($upload_files) ." total have successfully been uploaded. Here are the uploaded files: <br/><br/>" . print_r($files_uploaded) . "";
} else { return "Please a file or multiple files to upload."; }
}
?>Enjoy!